Decaffeinated coffee – when and where was it actually invented and how is decaffeinated coffee made?
WHAT IS CAFFEINE?
In order to answer these questions, we first want to clarify what caffeine actually is and why it can be useful to drink decaffeinated coffee. Caffeine is a naturally occurring compound that is also found in coffee plants. This is where the name caffeine comes from, as the chemical properties and effects of caffeine were first studied in detail using the coffee plant as an example.
Caffeine works by stimulating the release of the stress hormones cortisol and adrenaline. This increases blood pressure and heart rate. It takes 15 to 30 minutes for caffeine to enter the bloodstream and take effect. Therefore, decaffeinated coffee can be particularly useful for people who have high blood pressure.
WHEN AND WHERE WERE THE FIRST COFFEE BEANS DECAFFEINATED?
Decaffeinated coffee was first produced in 1903. The Bremen coffee merchant and founder of the Kaffee Hag company Ludwig Roselius developed the process named after him. The reason for this is very personal: his father died unexpectedly at the age of 59. Ludwig Roselius began researching the health effects of caffeine because doctors suspected his excessive coffee consumption was the cause of death.
Roselius first soaked the whole bean in a brine so that it could expand. To extract the caffeine, he added benzene to the beans. The Roselius process is no longer used today because the process involved the use of carcinogens.
METHODS THAT DECAFEINATE COFFEE BEANS
Decaffeinated coffee is an alternative for people who cannot tolerate coffee ingredients. This means that no one has to forgo the pleasure of coffee. But what processes can be used for this and how do they work?
SWISS WATER PROCESS
After the water has extracted the ingredients from the beans, the caffeine is filtered out of the water using activated charcoal. The caffeine is then removed from the new beans using added water. The unroasted coffee beans are soaked in hot water until all of the water-soluble components of the beans, such as caffeine, are in the water. After the water has extracted the ingredients from the beans, the caffeine is filtered out of the water using activated charcoal. The caffeine is then removed from the new beans using added water. After many repetitions, almost caffeine-free coffee is produced.
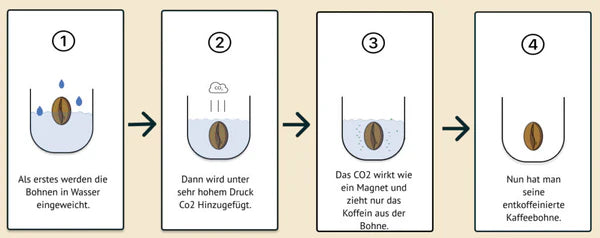
CARBON DIOXIDE PROCESS
Carbon dioxide is a natural component of the air. The beans are first softened with hot water, then placed under high pressure and rinsed with liquid or gaseous carbon dioxide. This isolates caffeine from the bean. No chemicals are used in this process.
INDIRECT METHOD
The indirect process of decaffeinating coffee beans is similar to the Roselius process. Here, too, the coffee beans are first soaked in water to extract all of the coffee beans' soluble components. The caffeine is then removed from the resulting water-coffee mixture. However, this is no longer done using benzene as in Ludwig Roselius' process, but rather with dichloromethane or ethyl acetate.
Finally, the decaffeinated water mixture is boiled with newly added beans. Only the caffeine is removed from the new beans, not the components that are important for the coffee aroma.
DIRECT PROCEDURE
In direct decaffeination, coffee beans are first exposed to steam and then soaked in a solvent for several hours. In a further step, the beans are separated from the solvent and dried for several hours to remove any residue.










DAS KÖNNTE DICH NOCH INTERESSIEREN
WIE SCHÄDLICH IST ENTKOFFEINIERTER KAFFEE?
According to a study, decaffeinated coffee has no negative effect on health. Decaffeinated coffee is even easier to tolerate. Too much caffeine or caffeine intolerance can have negative effects. The consequences can be shaking, rapid heartbeat, sweating and even stomach problems.
The method is also very important. If a decaffeinated coffee has the organic seal, you can be sure that no chemical solvents were used in the method. Our decaf coffee you can enjoy without any worries.
Many of the benefits of coffee are also retained in decaffeinated coffee. Coffee beans contain around 1,000 antioxidants. Antioxidants protect our cells from damage and thus contribute to a lower risk of disease.
CAN YOU DRINK DECAFFEINATED COFFEE DURING PREGNANCY?
Decaffeinated coffee can definitely be consumed during pregnancy without any concerns or danger. According to the EU regulation, decaffeinated coffee can only contain 0.1% caffeine. During pregnancy, 200 mg of caffeine can be consumed without any concerns. One cup of decaffeinated coffee contains around 2-5 mg of caffeine. To be precise, you could drink around 40 cups of decaffeinated coffee during pregnancy.
IS THERE A NATURALLY DECAFEINATED COFFEE BEAN?
The processes described require a lot of effort and money to remove the caffeine. In addition, the caffeine is necessary for the plant to deter pests with its bitter taste. But is there a coffee plant that already contains decaffeinated beans?
In fact, scientists in Ethiopia discovered a caffeine-free coffee plant. Since the discovery, various studies have been carried out. However, the results are not yet promising because the plant does not flower at the same time, which leads to irregular pollination.










